Sustainability InitiativesResponse to Climate Change: Disclosures based on the TCFD’s Recommendations
1. Sustainability Policy
In May 2022, the Group stated its support for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures(TCFD) as well as conducted a scenario analysis following these recommendations and examined countermeasures. The Group will now disclose information on its initiatives to address climate change, along with contributing to more resilient management and the realization of a sustainable international community.
The Group has been striving to preserve the global environment through the development of environmentally friendly products and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. In our 12th Medium-Term Management Plan, we aim to be a creative development-driven company that contributes to a sustainable society by supporting the world’s leading technologies with unique and superior products.

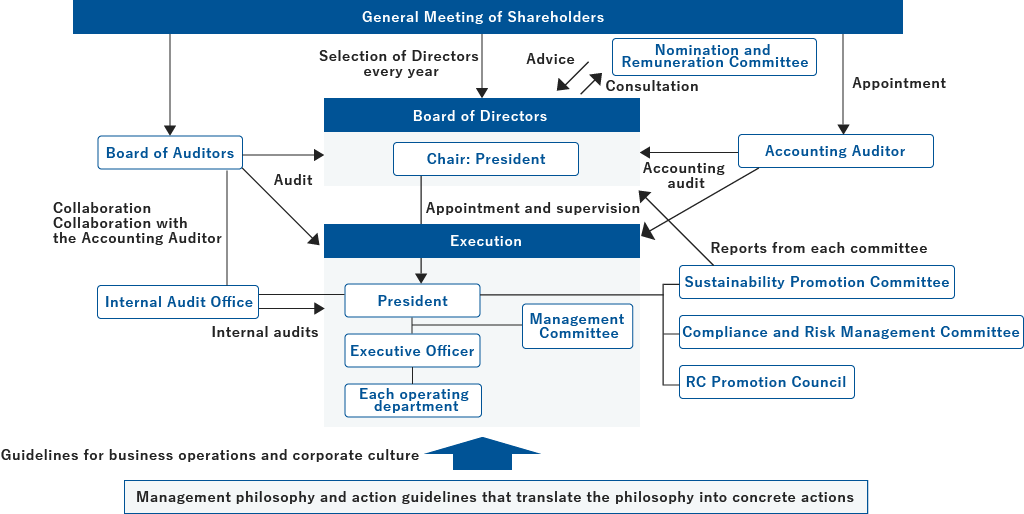
2. Governance
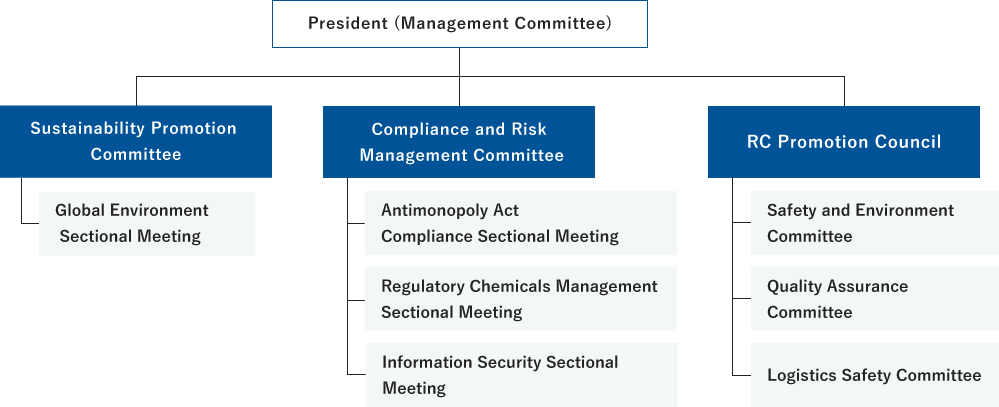
The Group has placed sustainability at the core of its management policy, including its response to climate change, and has established the Sustainability Promotion Committee, chaired by the President, to promote sustainability. In regard to the important theme of climate change issues, we established the Global Environment Sectional Meeting under the Sustainability Promotion Committee to handle our response to climate change, including the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Climate change related information is managed by the Sustainability Promotion Committee and Global Environment Sectional Meeting, which deliberate and determine specific targets. Details of these discussions are reported regularly to the Board of Directors (targeting at least twice a year) and, among them, matters approved by the Board of Directors are reflected in the Medium-Term Management Plan and annual plan. Additionally, the status of our response to climate change is monitored and managed by the Sustainability Promotion Committee, ensuring the progress is supervised continuously.
3. Strategy
The Group identifies risks and opportunities of climate change and evaluates the impacts on its business operations, with Sustainability Promotion Committee and Global Environment Sectional Meeting spearheading these efforts. In the evaluation of risks and opportunities, we conduct scenario analysis using multiple scenarios published by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Going forward, we will use analysis to explore impacts in 2030 assuming the following two world views.
Table. Scenarios used in Analysis and Sources
| 2°C (1.5°C) Scenario | 4°C Scenario |
|---|---|
| This scenario assumes that the impacts of policies and regulations will grow, resulting in more proactive efforts toward the transition to a decarbonized society so that the increase in average temperature will be limited to less than 2°C by 2100 compared to the Industrial Revolution. | This scenario assumes that governments’ climate change countermeasures will not go beyond current policies and regulations, and that the average temperature will rise by about 4°C in 2100 compared to the Industrial Revolution, resulting in greater physical impacts such as abnormal weather disasters. |
| (Referenced scenarios) Fifth Assessment Report of the IPCC (AR5) RCP2.6 IEA WEO2021 SDS, NZE2050 |
(Referenced scenarios) Fifth Assessment Report of the IPCC (AR5) RCP8.5 IEA WEO2021 STEPS |
2°C (1.5°C) Scenario Analysis
In the 2°C (1.5°C) scenario analysis, a variety of policies and regulations are expected to be introduced for the transition to a decarbonized society, and the Group recognizes that there are risks, including the financial impact of carbon taxes and reduced sales of our products due to diminished demand for products with a high global warming potential.
On the other hand, due to growing awareness of climate change, the market for lithium-ion batteries, which are indispensable for electric vehicles that will play a part in realizing a decarbonized society, is expected to expand, and as a result, demand for materials required to make lithium-ion batteries supplied by our company will also increase. We believe that this can be a great opportunity. Going forward, we will evaluate these risks and opportunities, both quantitatively and qualitatively, and examine countermeasures.
Table. Risks and Opportunities in Each Scenario
| Factors | Time horizon | Events | Classification | Response measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon pricing | Long-term | Increased costs related to business operations due to the introduction of carbon pricing, including carbon taxes | Risk | ・Energy conservation measures ・Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions ・Streamlining of energy use through product mix ・Transition to renewable energy ・Procurement of environmental value |
| Changes in energy costs | Medium to Long-term | Increased costs for purchasing electricity associated with the transition to renewable energy | Risk | ・Energy conservation measures ・Streamlining of energy use through product mix |
| Increased transportation costs due to soaring fossil fuel prices | Risk | ・Promote a modal shift ・Increased transportation lot sizes for improved logistics efficiency |
||
| Changes in demand for environmentally friendly products | Medium to Long-term | Decreased demand for high GWP products | Risk | ・Promote the development of environmentally friendly products |
| Growth of lithium-ion battery market | Opportunity | ・Strengthen capacity to produce battery materials in response to market growth ・Capture market growth through the expansion of the licensing business |
||
| Increased demand for environmentally friendly products including low GWP gas products, etc. | Opportunity | ・Promote the development of environmentally friendly products ・Strengthen production capacity to address the growing demand for environmentally friendly products |
||
| Changes in raw materials costs | Medium to Long-term | Rising procurement costs caused by complex factors | Risk | ・Promote recycling |
Definition of time horizons
Short-term: Less than 3 years; Medium-term: 3 years or more to less than 5 years; Long-term: 5 years or more
4°C Scenario Analysis
In the 4°C scenario analysis, extreme weather is expected to become more frequent and devastating, and the Group recognizes that possible flood damage at its domestic bases poses the greatest risk. In addition, damages incurred from the suspension of operations of our bases caused by flooding is also a risk. Going forward, we will evaluate these risks, both quantitatively and qualitatively, and examine countermeasures.
Table. Risks and Opportunities in Each Scenario
| Factors | Time horizon | Events | Classification | Response measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severity of extreme weather events | Short-term | Direct damages to the Company’s bases caused by flooding or tidal surge | Risk | ・Develop a risk management structure ・BCP measures ・Decentralization of production bases |
| Direct damages to the Company’s bases caused by flooding or tidal surge (Damages caused by suspension of operations due to damaged bases) |
||||
| Drought | Long-term | Further shortage of semiconductors resulting from droughts, leading to reduced sales opportunities of specialty gases and diminished sales | Risk | ・Sale of speciality gas to areas other than semiconductors ・Strengthen competitiveness |
| If the Shibukawa Plant consumes large amounts of industrial water, a water shortage could affect production activities, leading to diminished sales on reduced production capacity | ・R&D and investment to enhance water usage efficiency |
Definition of time horizons
Short-term: Less than 3 years; Medium-term: 3 years or more to less than 5 years; Long-term: 5 years or more
4. Risk Management
In its response to climate change, the Group, through the Sustainability Promotion Committee and Global Environment Sectional Meeting, evaluates risks and opportunities using scenario analysis and other methods after identifying expected climate change risks. In addition, we will address risks related to climate change countermeasures, such as energy conservation measures, and other important ESG issues through close collaboration with other committees as necessary. The Compliance and Risk Management Committee is responsible for labor environment and governance, while the RC Promotion Council is in charge of quality assurance, reduction of waste, and energy conservation measures. In this manner, we conduct risk management by continuously collecting information. Details of these deliberations are regularly reported to the Board of Directors and discussed countermeasures are reflected in business activities to improve risk management.
5. Indicators and Targets
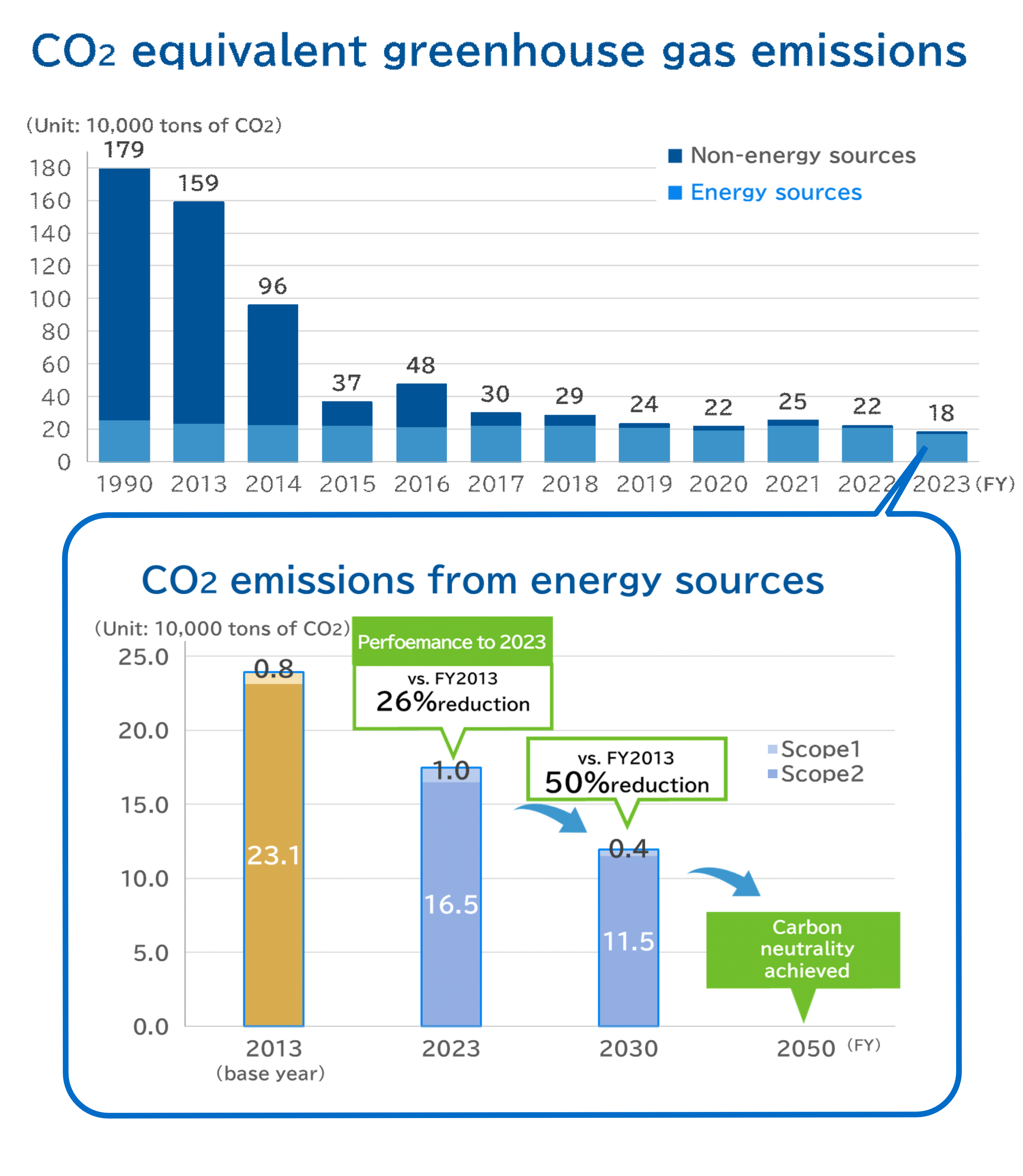
Existing Initiatives
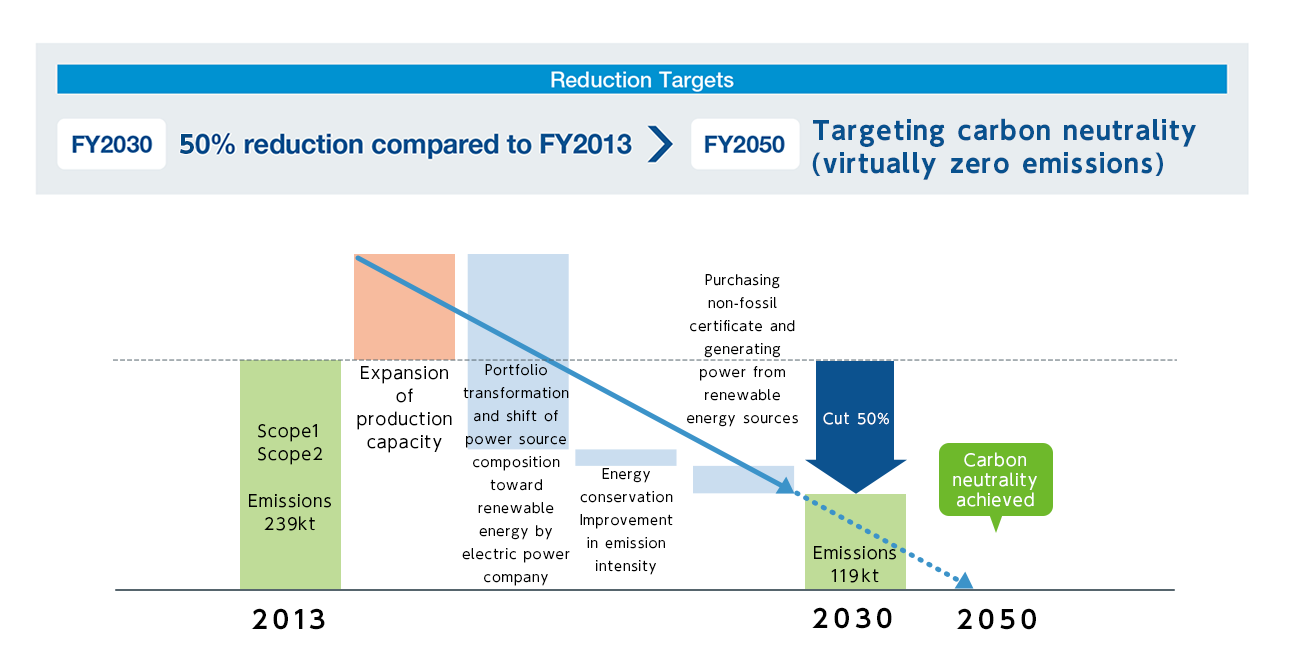
We have been working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from non-energy sources since 2009 with the introduction of abatement equipment, and have made significant progress. We are also working to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases from energy sources by improving production efficiency.
>For more information, please see “Responding to Climate Change”.
New Initiatives toward Carbon Neutrality
We have been promoting sustainability activities, reducing energy-intensive products, and strengthening our commitment to decarbonization and recycling as one of the key strategies of our 12th Medium-Term Management Plan Dominate 1000 since FY2022 to enhance social value.
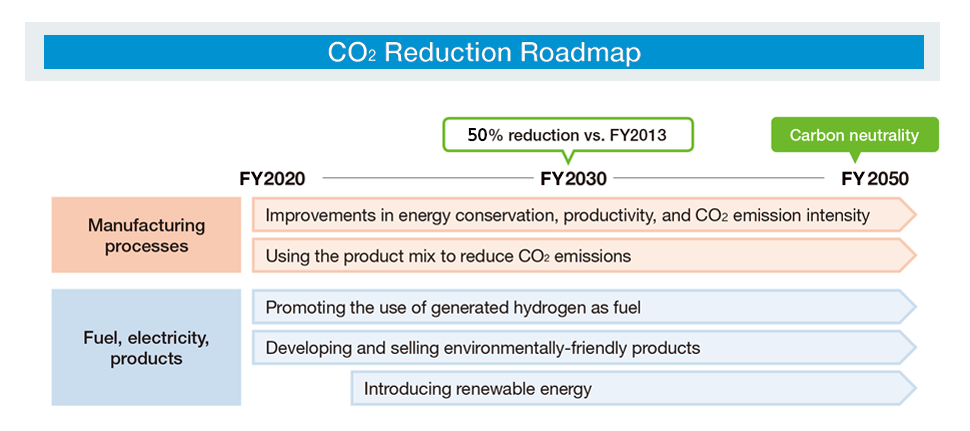
In order to contribute to the creation of a sustainable society, we have set a new long-term target to reduce our energy-derived greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 and 2) in 2030 by 50% compared to 2013, and we will accelerate the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
Vision toward 2030 and Policies for Main Initiatives and Policies
Our vision is to accelerate the expansion of precision chemicals by further advancing fine chemicals, promote the development of technology for greenhouse gas emission reduction and decarbonization, and become a creative development-driven company that contributes to a sustainable society. Toward this end, we are carrying out the following as policies for main initiatives.
- 1. Improve CO2 emission intensity while achieving growth in the fine chemicals business
- 2. Introduction of renewable energy
- 3. Product mix (in addition to productivity improvement and portfolio restructuring)
- 4. Promote the development of environmentally friendly products
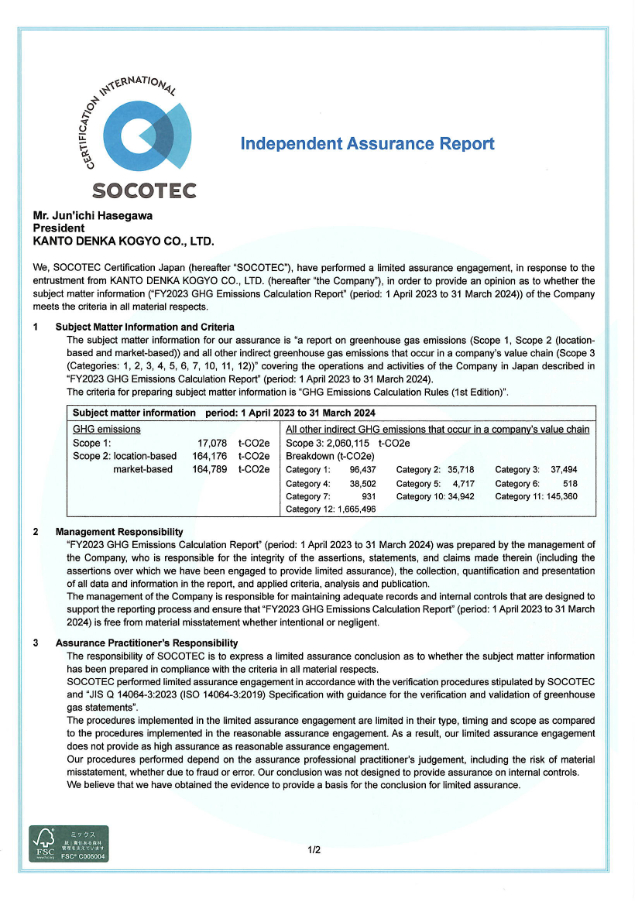
6. Third-party Verification and Assurance
We received third-party verification and assurance for our environment-related data from SOCOTEC Certification Japan. in September 2024. Please see PDF for details.
> Independent Assurance Report